Code Complexity: Metrics, Causes, and Smart Fixes
Dec 12, 2025
Dec 12, 2025
Earlier this year, McKinsey ran the numbers on modernization pain points, and one quiet culprit kept showing up in every postmortem: creeping complexity that hides across files and decisions, not in flashy algorithmic edge cases.
You know this script: a tiny change in a legacy module turns into a three-day review, or a bug resurfaces because the original intent is nowhere in the code. It’s not about blame, it’s about time lost.
Engineers can spend as much as 42% of their workweek dealing with maintenance, refactors, and the fallout of past shortcuts, which makes complexity an operational risk, not just a code smell.
If this friction feels familiar, it’s not incidental. This guide breaks down the metrics that actually matter, the root causes teams often overlook, and the smart, reliable fixes that bring complexity back under control.
Overview
Complexity as a delivery risk: It consumes up to 42% of developer time, making it a measurable threat to velocity and reliability.
Metrics that matter: Cyclomatic complexity, cognitive complexity, coupling, and churn offer the clearest signals of rising code complexity.
Root causes to watch: Feature creep, architectural drift, deferred refactoring, and knowledge loss quietly drive complexity across the codebase.
Team-wide impact: Rising complexity increases lead times, change-failure rates, MTTR, onboarding effort, and overall operational drag.
Smart prevention strategy: Small, targeted refactors paired with automated PR guardrails (like Entelligence AI) stop complexity before it spreads.
What Is Code Complexity?
Code complexity describes measurable traits that raise cognitive load, regression risk, and maintenance cost. It’s not just LOC; it’s how hard a change is to reason about, verify, and ship safely.
Watch for these concrete signals in PRs, test runs, and incident reports:
Long functions with mixed responsibilities.
Deep nesting and branching logic.
Execution paths split across many files.
Files with high churn or frequent reverts.
Tests that need heavy mocking or full integration setups.
Tight coupling that causes ripple effects.
Vague names and missing intent comments.
Understanding these signals is only the starting point; the next step is quantifying them with the metrics that actually matter.
Key Metrics Used to Measure Code Complexity
While “complexity” often feels like a subjective judgement, engineering teams increasingly rely on objective, code-driven metrics to detect trouble spots early. These metrics help flag code that’s likely to be hard to test, error-prone, or difficult for new maintainers to understand.
Below is a breakdown of the most useful metrics across different dimensions and what each reveals about the health of your codebase.
Metric | What It Measures | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
Cyclomatic Complexity | Number of decision paths in a function. | More branches = harder testing and higher error risk. |
Halstead Metrics | Operator/operand counts and derived “effort.” | Indicates cognitive load and maintainability effort. |
Lines of Code (LOC) | Executable line count. | Larger units tend to hide bugs and slow reviews. |
Maintainability Index | Composite score (CC + Halstead + LOC). | Quick signal of overall maintainability health. |
Cognitive Complexity | How hard code is to mentally follow. | Predicts reviewer fatigue and misunderstanding. |
Coupling Metrics | Degree of inter-module dependencies. | High coupling increases ripple effects and refactor risk. |
Suggested Read: Essential Metrics for Measuring Code Quality
Metrics reveal where complexity lives, but the harder question is what’s causing it.
Why Code Complexity Happens: The Real Causes
Complexity usually surfaces not in dramatic failures, but in the quiet accumulation of mismatched patterns, architectural drift, and decisions made under shifting constraints.
It’s the friction that appears when intent, structure, and scale start pulling in different directions. Understanding why this drift happens is the only way to prevent complexity from becoming the default state of the codebase.
Here are the most common and research-backed reasons complexity accumulates in codebases:
Deadline pressure & time-to-market demands: Fast shipping often turns “temporary” fixes into permanent debt, especially when refactors get postponed.
Evolving requirements and feature creep: As features stack up, the underlying design rarely gets revisited, leading to tangled logic and unintended complexity.
Insufficient refactoring or delayed cleanup: Quick patches add up. Without regular cleanup, clarity erodes, and maintenance effort rises.
Poor design or architectural choices: Tightly coupled modules, oversized services, or early framework decisions can lock teams into complexity that’s hard to unwind later.
Lack of testing or weak automation: When tests are thin, developers rely on shortcuts that introduce unpredictable behavior and fragile code paths.
Team changes and lost context: As people move on and documentation lags, parts of the codebase become “mystery zones,” increasing cognitive load and slowing safe changes.

Once these root causes are in play, their effects don’t stay confined to the code; they show up across the entire engineering workflow.
How Code Complexity Impacts Engineering Teams
Teams often feel the symptoms long before they can name the source: PRs that stall without an obvious reason, incidents that take hours longer to triage, and delivery timelines that slip even when headcount grows.
This section shows how complexity turns into measurable friction and how to catch warning signs before they become costly to unwind.
Longer lead time for changes: Reviews take more passes, tests require heavier setups, and even small updates become multi-step efforts.
Higher change-failure rate: Fragile, interdependent areas make deployments riskier and increase the likelihood of rollbacks or hotfixes.
Slower incident resolution: Untangling logic during outages takes longer when code paths are unclear or spread across multiple modules.
More engineering time spent on maintenance: A growing share of work shifts toward patching, stabilizing, and deciphering older logic instead of shipping new value.
Unreliable or brittle tests: Complex code creates flaky tests, long CI cycles, and reduced confidence in release readiness.
Onboarding friction and bottlenecks: New engineers take longer to ramp up, while legacy areas concentrate knowledge in a few individuals, creating delivery risks.
Complexity is easiest to control when it’s caught at the PR stage rather than after it spreads. Entelligence AI gives you that visibility. Book a demo to see how it transforms your review workflow!
Seeing how complexity affects delivery makes one thing clear: it’s time to focus on the practices that reliably reduce it.
Smart Fixes: Practical Ways to Reduce Code Complexity
Complexity usually breaks down fastest through small, intentional shifts in how code is shaped, named, and structured in everyday work. These fixes aren’t theoretical patterns; they’re the practical moves senior engineers reach for when they need clarity now without slowing the sprint.
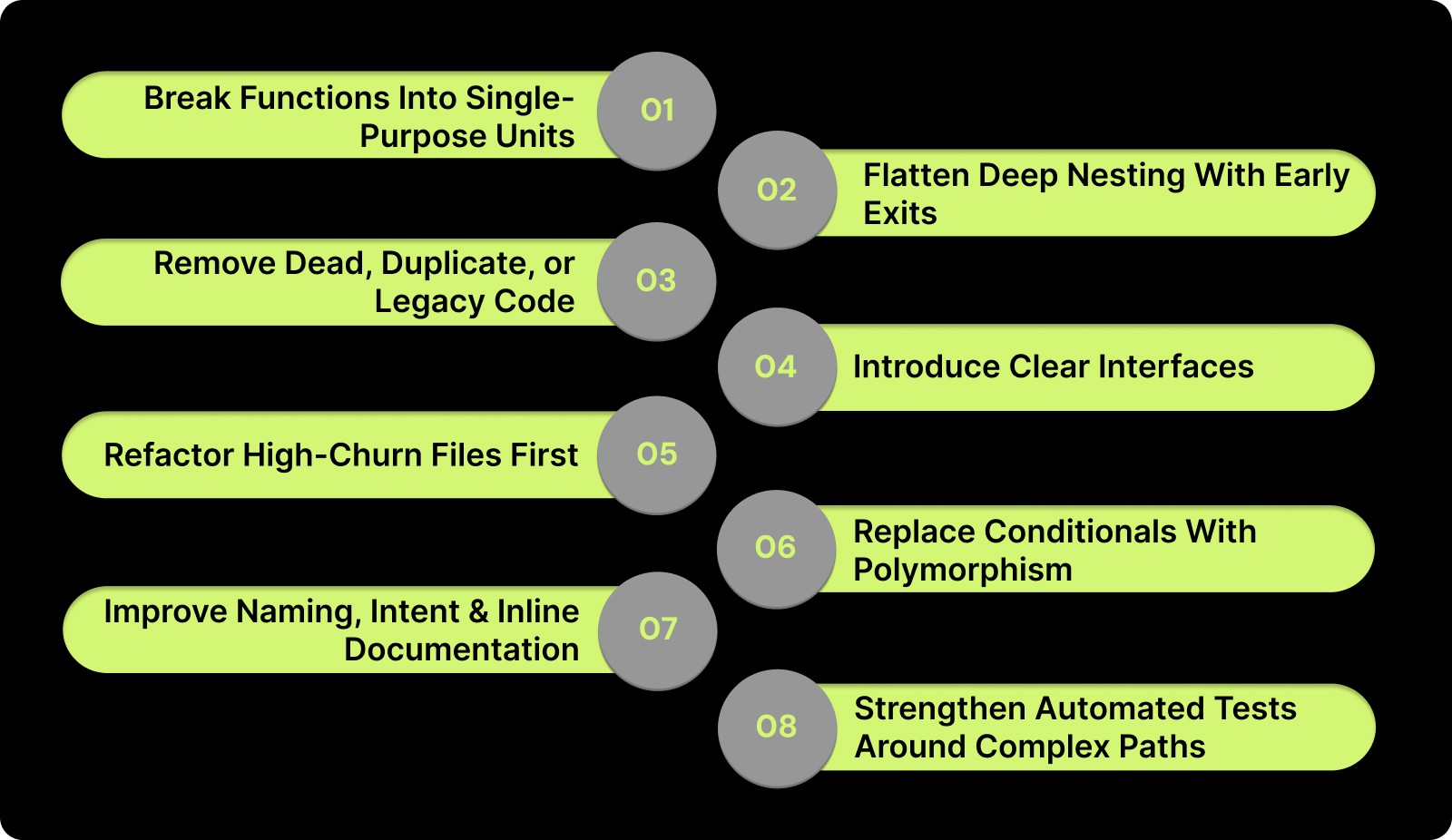
The following techniques focus on changes that deliver immediate impact while naturally preventing complexity from creeping back in.
1. Break Functions Into Single-Purpose Units
Splitting large, mixed-responsibility functions into focused units that do one thing clearly.
How it helps: Reduces mental load, clarifies intent, and makes code paths easier to test.
How to do it: Identify functions with multiple branching paths or repeated context switching and extract each logical step into its own named function.
2. Flatten Deep Nesting With Early Exits
Replacing layers of nested conditionals with guard clauses (return early if invalid).
How it helps: Simplifies control flow, reduces branching, and makes edge cases obvious.
How to do it: Scan for deeply indented blocks, invert the condition, and return early to keep the main logic straight-line.
3. Remove Dead, Duplicate, or Legacy Code
Cleaning out unused functions, redundant utilities, outdated branches, and abandoned abstractions.
How it helps: Shrinks the code surface area, reduces reviewer burden, and cuts down on accidental dependency chains.
How to do it: Use static analysis, code search, and version history to confirm unreferenced code and remove it with confidence.
4. Introduce Clear Interfaces and Localize Side Effects
Ensuring modules expose clean entry points while keeping mutations and I/O operations predictable.
How it helps: Limits unexpected behavior, reduces coupling, and makes modules easier to refactor independently.
How to do it: Encapsulate state changes, use well-named public functions, and isolate external calls (DB, APIs) to specific layers.
5. Refactor High-Churn Files First
Prioritizing refactors in files that change frequently rather than those that are merely messy.
How it helps: Maximizes ROI by reducing future conflict risk, merging complexity, and regressions in high-traffic areas.
How to do it: Look for files with consistent PR activity, repeated comments, or incident references, and stabilize those first.
6. Replace Conditionals With Polymorphism or Strategy Patterns
Converting sprawling if/else or switch blocks into object- or function-based behavior selection.
How it helps: Simplifies branching, isolates variations, and reduces the chance of logic drifting across cases.
How to do it: Identify conditionals controlling behavior types and introduce a strategy map or small class hierarchy.
7. Improve Naming, Intent, and Inline Documentation
Using clear, precise names and short comments that explain why, not what.
How it helps: Reduces cognitive complexity for reviewers and new contributors.
How to do it: Rename ambiguous variables/functions, add one-line intent notes for non-obvious logic, and remove outdated comments.
8. Strengthen Automated Tests Around Complex Paths
Adding targeted tests for edge cases, boundary conditions, and high-risk logic.
How it helps: Makes future simplification safer and reveals hidden assumptions.
How to do it: Prioritize tests for code with frequent regressions, heavy branching, or unclear responsibilities.

Even with solid engineering practices, complexity still slips through, especially in fast-moving teams. That’s where intelligent tooling can make a measurable difference.
How Entelligence AI Simplifies Complexity in Pull Requests
For many teams, PR reviews are the bottleneck where complexity meets context-switching and delay. Entelligence AI transforms that choke point into an engine of clarity and velocity.
It doesn’t just flag issues; it understands the full codebase, enforces team standards, and gives actionable feedback where it matters, so code reviews become a productivity accelerator rather than a roadblock.
How Entelligence Helps:
Context-Aware Automated Reviews
Entelligence analyzes code changes in the context of the entire repository. It surfaces not just syntactic issues, but hidden complexity, duplication, or risky patterns, giving feedback as soon as a PR is opened.Real-Time Feedback in Your IDE
With its IDE integration (e.g., for VS Code), developers get instant review suggestions while writing code, catching complexity early, before it even enters a PR. Saves time and reduces refactor burden later.Auto-Fix Suggestions & Quick Refactors
Rather than leaving vague warnings, Entelligence often provides committable code fixes or concrete refactoring recommendations. This is so that cleanup and simplification become quick and action-oriented.Consistent Quality & Team-Wide Standards
It enforces coding standards and team policies automatically, across all PRs. This eliminates variance from manual reviews and ensures complexity doesn’t creep in unnoticed.Visibility, Analytics & Long-Term Insights
Through dashboards and history tracking, Entelligence offers data on code quality trends, redundant code hotspots, refactoring opportunities, and team velocity. This helps teams plan refactors proactively rather than reactively.
Must Read: How to Use AI for Code Reviews on GitHub?
With the right tooling in place, the next step is adopting a structured plan that keeps complexity under control across the entire codebase.
A Step-by-Step Plan to Manage Complexity Across Your Codebase
High-performing teams take the opposite approach: they build a predictable rhythm around complexity so it never gets a chance to dominate the codebase. Here’s a structured plan you can apply without slowing delivery.
1. Establish a Baseline Before You Touch Anything
Map out where complexity currently lives: high-churn files, modules tied to recurring incidents, routes with heavy branching, or areas that repeatedly stall PRs. Treat this as a diagnostic snapshot, not a judgment.
2. Define What “Too Complex” Means for Your Team
Create practical thresholds — maximum function size, acceptable nesting depth, preferred patterns, and test expectations for high-risk logic. Setting these norms upfront prevents debates later and gives reviewers a shared language.
3. Target the Areas With the Highest Future Impact
Don’t refactor everything. Start with the code that’s touched weekly, not yearly. Improvements here reduce long-term drag far more than polishing forgotten files.
4. Pair Fixes With Active Work Instead of Side Projects
The easiest place to reduce complexity is inside work that’s already happening. When a feature touches a messy module, tidy the complexity that directly relates to that change. This keeps refactors small, contextual, and politically easy to ship.
5. Introduce Automated Guardrails at the PR Level
Use tools (like Entelligence) to catch complexity growth automatically: rising cognitive load, unnecessary nesting, duplication, or unclear logic. Guardrails make complexity prevention effortless and consistent.
6. Review Trends, Not Just Individual Changes
Look at month-over-month patterns: which areas are stabilizing, which keep drifting, and where PR reviewers still hesitate. Trend-based insights help you invest in the right refactors at the right time.
7. Revisit Standards Quarterly as the System Evolves
Complexity is dynamic. What felt “fine” three months ago may slow you down now. Refresh thresholds and patterns as the codebase, team, and product mature.
Also Read: Exploring PR Review AI Tools: Boost Code Quality Fast

Conclusion
Complexity will always evolve as your system grows, but the teams that stay ahead are the ones that treat clarity as a continuous practice, not an occasional clean-up. The real advantage comes from building habits that let you see complexity early, respond deliberately, and preserve momentum even as the codebase expands.
That’s exactly where Entelligence AI becomes a strategic multiplier. By surfacing issues the moment they form, guiding developers with real-time context, and enforcing consistency across PRs, it creates an environment where complexity is managed before it turns into a drag. It gives teams the visibility and feedback loops needed to maintain a healthy codebase at scale.
If you’re ready to simplify reviews, reduce risk, and ship cleaner code with far less effort, book a demo with Entelligence AI.
FAQs
1. What is the fastest way to identify rising code complexity in a large codebase?
Use a combination of churn analysis, PR review patterns, and automated tools that surface complexity hotspots. High-churn files and repeated reviewer confusion are usually the earliest signals.
2. How do I know when code complexity is high enough to require refactoring?
If a module consistently slows reviews, breaks unrelated functionality, or requires extensive mocking to test, its complexity has exceeded the cost threshold, and refactoring becomes cheaper than leaving it as-is.
3. Does reducing code complexity always require major rewrites?
No. Most gains come from small, targeted improvements: splitting oversized functions, removing dead code, flattening conditionals, and clarifying interfaces.
4. How does code complexity impact engineering velocity over time?
As complexity grows, lead times, change-failure rates, MTTR, and onboarding time all increase. The compounding effect is what often causes velocity drops even when teams scale headcount.
5. Can tools like Entelligence AI actually prevent code complexity from growing?
Yes. By surfacing risks at the PR stage, enforcing standards, and providing auto-fix suggestions, tools like Entelligence catch complexity before it spreads, making long-term control far easier.
Earlier this year, McKinsey ran the numbers on modernization pain points, and one quiet culprit kept showing up in every postmortem: creeping complexity that hides across files and decisions, not in flashy algorithmic edge cases.
You know this script: a tiny change in a legacy module turns into a three-day review, or a bug resurfaces because the original intent is nowhere in the code. It’s not about blame, it’s about time lost.
Engineers can spend as much as 42% of their workweek dealing with maintenance, refactors, and the fallout of past shortcuts, which makes complexity an operational risk, not just a code smell.
If this friction feels familiar, it’s not incidental. This guide breaks down the metrics that actually matter, the root causes teams often overlook, and the smart, reliable fixes that bring complexity back under control.
Overview
Complexity as a delivery risk: It consumes up to 42% of developer time, making it a measurable threat to velocity and reliability.
Metrics that matter: Cyclomatic complexity, cognitive complexity, coupling, and churn offer the clearest signals of rising code complexity.
Root causes to watch: Feature creep, architectural drift, deferred refactoring, and knowledge loss quietly drive complexity across the codebase.
Team-wide impact: Rising complexity increases lead times, change-failure rates, MTTR, onboarding effort, and overall operational drag.
Smart prevention strategy: Small, targeted refactors paired with automated PR guardrails (like Entelligence AI) stop complexity before it spreads.
What Is Code Complexity?
Code complexity describes measurable traits that raise cognitive load, regression risk, and maintenance cost. It’s not just LOC; it’s how hard a change is to reason about, verify, and ship safely.
Watch for these concrete signals in PRs, test runs, and incident reports:
Long functions with mixed responsibilities.
Deep nesting and branching logic.
Execution paths split across many files.
Files with high churn or frequent reverts.
Tests that need heavy mocking or full integration setups.
Tight coupling that causes ripple effects.
Vague names and missing intent comments.
Understanding these signals is only the starting point; the next step is quantifying them with the metrics that actually matter.
Key Metrics Used to Measure Code Complexity
While “complexity” often feels like a subjective judgement, engineering teams increasingly rely on objective, code-driven metrics to detect trouble spots early. These metrics help flag code that’s likely to be hard to test, error-prone, or difficult for new maintainers to understand.
Below is a breakdown of the most useful metrics across different dimensions and what each reveals about the health of your codebase.
Metric | What It Measures | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
Cyclomatic Complexity | Number of decision paths in a function. | More branches = harder testing and higher error risk. |
Halstead Metrics | Operator/operand counts and derived “effort.” | Indicates cognitive load and maintainability effort. |
Lines of Code (LOC) | Executable line count. | Larger units tend to hide bugs and slow reviews. |
Maintainability Index | Composite score (CC + Halstead + LOC). | Quick signal of overall maintainability health. |
Cognitive Complexity | How hard code is to mentally follow. | Predicts reviewer fatigue and misunderstanding. |
Coupling Metrics | Degree of inter-module dependencies. | High coupling increases ripple effects and refactor risk. |
Suggested Read: Essential Metrics for Measuring Code Quality
Metrics reveal where complexity lives, but the harder question is what’s causing it.
Why Code Complexity Happens: The Real Causes
Complexity usually surfaces not in dramatic failures, but in the quiet accumulation of mismatched patterns, architectural drift, and decisions made under shifting constraints.
It’s the friction that appears when intent, structure, and scale start pulling in different directions. Understanding why this drift happens is the only way to prevent complexity from becoming the default state of the codebase.
Here are the most common and research-backed reasons complexity accumulates in codebases:
Deadline pressure & time-to-market demands: Fast shipping often turns “temporary” fixes into permanent debt, especially when refactors get postponed.
Evolving requirements and feature creep: As features stack up, the underlying design rarely gets revisited, leading to tangled logic and unintended complexity.
Insufficient refactoring or delayed cleanup: Quick patches add up. Without regular cleanup, clarity erodes, and maintenance effort rises.
Poor design or architectural choices: Tightly coupled modules, oversized services, or early framework decisions can lock teams into complexity that’s hard to unwind later.
Lack of testing or weak automation: When tests are thin, developers rely on shortcuts that introduce unpredictable behavior and fragile code paths.
Team changes and lost context: As people move on and documentation lags, parts of the codebase become “mystery zones,” increasing cognitive load and slowing safe changes.

Once these root causes are in play, their effects don’t stay confined to the code; they show up across the entire engineering workflow.
How Code Complexity Impacts Engineering Teams
Teams often feel the symptoms long before they can name the source: PRs that stall without an obvious reason, incidents that take hours longer to triage, and delivery timelines that slip even when headcount grows.
This section shows how complexity turns into measurable friction and how to catch warning signs before they become costly to unwind.
Longer lead time for changes: Reviews take more passes, tests require heavier setups, and even small updates become multi-step efforts.
Higher change-failure rate: Fragile, interdependent areas make deployments riskier and increase the likelihood of rollbacks or hotfixes.
Slower incident resolution: Untangling logic during outages takes longer when code paths are unclear or spread across multiple modules.
More engineering time spent on maintenance: A growing share of work shifts toward patching, stabilizing, and deciphering older logic instead of shipping new value.
Unreliable or brittle tests: Complex code creates flaky tests, long CI cycles, and reduced confidence in release readiness.
Onboarding friction and bottlenecks: New engineers take longer to ramp up, while legacy areas concentrate knowledge in a few individuals, creating delivery risks.
Complexity is easiest to control when it’s caught at the PR stage rather than after it spreads. Entelligence AI gives you that visibility. Book a demo to see how it transforms your review workflow!
Seeing how complexity affects delivery makes one thing clear: it’s time to focus on the practices that reliably reduce it.
Smart Fixes: Practical Ways to Reduce Code Complexity
Complexity usually breaks down fastest through small, intentional shifts in how code is shaped, named, and structured in everyday work. These fixes aren’t theoretical patterns; they’re the practical moves senior engineers reach for when they need clarity now without slowing the sprint.

The following techniques focus on changes that deliver immediate impact while naturally preventing complexity from creeping back in.
1. Break Functions Into Single-Purpose Units
Splitting large, mixed-responsibility functions into focused units that do one thing clearly.
How it helps: Reduces mental load, clarifies intent, and makes code paths easier to test.
How to do it: Identify functions with multiple branching paths or repeated context switching and extract each logical step into its own named function.
2. Flatten Deep Nesting With Early Exits
Replacing layers of nested conditionals with guard clauses (return early if invalid).
How it helps: Simplifies control flow, reduces branching, and makes edge cases obvious.
How to do it: Scan for deeply indented blocks, invert the condition, and return early to keep the main logic straight-line.
3. Remove Dead, Duplicate, or Legacy Code
Cleaning out unused functions, redundant utilities, outdated branches, and abandoned abstractions.
How it helps: Shrinks the code surface area, reduces reviewer burden, and cuts down on accidental dependency chains.
How to do it: Use static analysis, code search, and version history to confirm unreferenced code and remove it with confidence.
4. Introduce Clear Interfaces and Localize Side Effects
Ensuring modules expose clean entry points while keeping mutations and I/O operations predictable.
How it helps: Limits unexpected behavior, reduces coupling, and makes modules easier to refactor independently.
How to do it: Encapsulate state changes, use well-named public functions, and isolate external calls (DB, APIs) to specific layers.
5. Refactor High-Churn Files First
Prioritizing refactors in files that change frequently rather than those that are merely messy.
How it helps: Maximizes ROI by reducing future conflict risk, merging complexity, and regressions in high-traffic areas.
How to do it: Look for files with consistent PR activity, repeated comments, or incident references, and stabilize those first.
6. Replace Conditionals With Polymorphism or Strategy Patterns
Converting sprawling if/else or switch blocks into object- or function-based behavior selection.
How it helps: Simplifies branching, isolates variations, and reduces the chance of logic drifting across cases.
How to do it: Identify conditionals controlling behavior types and introduce a strategy map or small class hierarchy.
7. Improve Naming, Intent, and Inline Documentation
Using clear, precise names and short comments that explain why, not what.
How it helps: Reduces cognitive complexity for reviewers and new contributors.
How to do it: Rename ambiguous variables/functions, add one-line intent notes for non-obvious logic, and remove outdated comments.
8. Strengthen Automated Tests Around Complex Paths
Adding targeted tests for edge cases, boundary conditions, and high-risk logic.
How it helps: Makes future simplification safer and reveals hidden assumptions.
How to do it: Prioritize tests for code with frequent regressions, heavy branching, or unclear responsibilities.

Even with solid engineering practices, complexity still slips through, especially in fast-moving teams. That’s where intelligent tooling can make a measurable difference.
How Entelligence AI Simplifies Complexity in Pull Requests
For many teams, PR reviews are the bottleneck where complexity meets context-switching and delay. Entelligence AI transforms that choke point into an engine of clarity and velocity.
It doesn’t just flag issues; it understands the full codebase, enforces team standards, and gives actionable feedback where it matters, so code reviews become a productivity accelerator rather than a roadblock.
How Entelligence Helps:
Context-Aware Automated Reviews
Entelligence analyzes code changes in the context of the entire repository. It surfaces not just syntactic issues, but hidden complexity, duplication, or risky patterns, giving feedback as soon as a PR is opened.Real-Time Feedback in Your IDE
With its IDE integration (e.g., for VS Code), developers get instant review suggestions while writing code, catching complexity early, before it even enters a PR. Saves time and reduces refactor burden later.Auto-Fix Suggestions & Quick Refactors
Rather than leaving vague warnings, Entelligence often provides committable code fixes or concrete refactoring recommendations. This is so that cleanup and simplification become quick and action-oriented.Consistent Quality & Team-Wide Standards
It enforces coding standards and team policies automatically, across all PRs. This eliminates variance from manual reviews and ensures complexity doesn’t creep in unnoticed.Visibility, Analytics & Long-Term Insights
Through dashboards and history tracking, Entelligence offers data on code quality trends, redundant code hotspots, refactoring opportunities, and team velocity. This helps teams plan refactors proactively rather than reactively.
Must Read: How to Use AI for Code Reviews on GitHub?
With the right tooling in place, the next step is adopting a structured plan that keeps complexity under control across the entire codebase.
A Step-by-Step Plan to Manage Complexity Across Your Codebase
High-performing teams take the opposite approach: they build a predictable rhythm around complexity so it never gets a chance to dominate the codebase. Here’s a structured plan you can apply without slowing delivery.
1. Establish a Baseline Before You Touch Anything
Map out where complexity currently lives: high-churn files, modules tied to recurring incidents, routes with heavy branching, or areas that repeatedly stall PRs. Treat this as a diagnostic snapshot, not a judgment.
2. Define What “Too Complex” Means for Your Team
Create practical thresholds — maximum function size, acceptable nesting depth, preferred patterns, and test expectations for high-risk logic. Setting these norms upfront prevents debates later and gives reviewers a shared language.
3. Target the Areas With the Highest Future Impact
Don’t refactor everything. Start with the code that’s touched weekly, not yearly. Improvements here reduce long-term drag far more than polishing forgotten files.
4. Pair Fixes With Active Work Instead of Side Projects
The easiest place to reduce complexity is inside work that’s already happening. When a feature touches a messy module, tidy the complexity that directly relates to that change. This keeps refactors small, contextual, and politically easy to ship.
5. Introduce Automated Guardrails at the PR Level
Use tools (like Entelligence) to catch complexity growth automatically: rising cognitive load, unnecessary nesting, duplication, or unclear logic. Guardrails make complexity prevention effortless and consistent.
6. Review Trends, Not Just Individual Changes
Look at month-over-month patterns: which areas are stabilizing, which keep drifting, and where PR reviewers still hesitate. Trend-based insights help you invest in the right refactors at the right time.
7. Revisit Standards Quarterly as the System Evolves
Complexity is dynamic. What felt “fine” three months ago may slow you down now. Refresh thresholds and patterns as the codebase, team, and product mature.
Also Read: Exploring PR Review AI Tools: Boost Code Quality Fast

Conclusion
Complexity will always evolve as your system grows, but the teams that stay ahead are the ones that treat clarity as a continuous practice, not an occasional clean-up. The real advantage comes from building habits that let you see complexity early, respond deliberately, and preserve momentum even as the codebase expands.
That’s exactly where Entelligence AI becomes a strategic multiplier. By surfacing issues the moment they form, guiding developers with real-time context, and enforcing consistency across PRs, it creates an environment where complexity is managed before it turns into a drag. It gives teams the visibility and feedback loops needed to maintain a healthy codebase at scale.
If you’re ready to simplify reviews, reduce risk, and ship cleaner code with far less effort, book a demo with Entelligence AI.
FAQs
1. What is the fastest way to identify rising code complexity in a large codebase?
Use a combination of churn analysis, PR review patterns, and automated tools that surface complexity hotspots. High-churn files and repeated reviewer confusion are usually the earliest signals.
2. How do I know when code complexity is high enough to require refactoring?
If a module consistently slows reviews, breaks unrelated functionality, or requires extensive mocking to test, its complexity has exceeded the cost threshold, and refactoring becomes cheaper than leaving it as-is.
3. Does reducing code complexity always require major rewrites?
No. Most gains come from small, targeted improvements: splitting oversized functions, removing dead code, flattening conditionals, and clarifying interfaces.
4. How does code complexity impact engineering velocity over time?
As complexity grows, lead times, change-failure rates, MTTR, and onboarding time all increase. The compounding effect is what often causes velocity drops even when teams scale headcount.
5. Can tools like Entelligence AI actually prevent code complexity from growing?
Yes. By surfacing risks at the PR stage, enforcing standards, and providing auto-fix suggestions, tools like Entelligence catch complexity before it spreads, making long-term control far easier.
We raised $5M to run your Engineering team on Autopilot
We raised $5M to run your Engineering team on Autopilot
Watch our launch video
Talk to Sales
Turn engineering signals into leadership decisions
Connect with our team to see how Entelliegnce helps engineering leaders with full visibility into sprint performance, Team insights & Product Delivery
Talk to Sales
Turn engineering signals into leadership decisions
Connect with our team to see how Entelliegnce helps engineering leaders with full visibility into sprint performance, Team insights & Product Delivery
Try Entelligence now